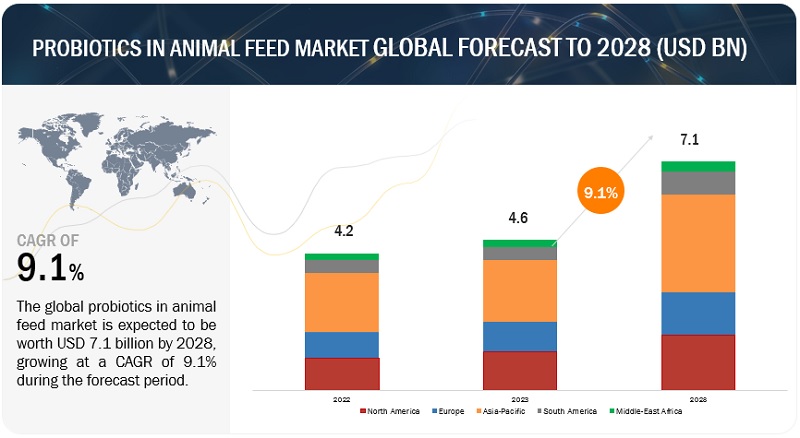
According to a research report "Probiotics in Animal Feed Market by Livestock (Poultry, Swine, Ruminants, Aquaculture, Pets), Source (Bacteria, Yeast, Fungi), Form (Dry, Liquid), Function (Qualitative) (Nutrition, Gut Health, Immunity, Productivity) Region - Global Forecast to 2028" published by MarketsandMarkets, the probiotics in animal feed market is projected to reach USD 7.1 billion by 2028 from USD 4.6 billion by 2023, at a CAGR of 9.1% during the forecast period in terms of value. The market for probiotics in animal feed is experiencing growth due to the increasing demand for meat and meat products among the growing population.
Download PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=85832335
Increase in demand for animal protein among consumers to drive the market growth of probiotics in animal feed
Probiotic offers solutions to enhance animal performance, improve animal health, reduce diseases risks, and align with the consumer preference for healthy and sustainable products. As livestock producers strive to meet the increasing demand of meat products, probiotics can play a vital role in optimizing the animal nutrition and wellbeing. In order to meet growing demand the livestock producers often rely on intensive production practices that might lead to various challenges such as stress, poor nutrition, and others. Probiotics, thus offers a potential solution by improving the gut health, increasing the nutrient absorption, and bolstering the immune system of animals. Thus, the demand for probiotics in animal feed could grow as livestock producers seeks to maximize productivity and optimize the health of animals.
By source, bacteria holds a significant market share during the forecast period
The most common microorganisms used as probiotics in livestock production are Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) from the genus Lactobacillus, Pediococcus, Lactococcus, Enterococcus, Streptococcus, and Leuconostoc. Nevertheless, only the genera Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Pediococcus, Enterococcus, and Weissella are the most frequently used in poultry production.
Bacteria dominated the probiotics in animal feed market as a source. This is because the segment has been studied and researched up on since a long time. Bacteria as raw materials are largely commercialized in the market which makes bacteria-based probiotics more familiar to customers. Moreover, scientific factors such as better bile (acid) resistance as compared to yeast, lets the bacteria-based probiotic product reach intestine and colon, where it is the most effective. All the stated factors are fueling the growth of the bacteria segment in probiotics in the animal feed market.
Request Sample Pages: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/requestsampleNew.asp?id=85832335
Asia Pacific to boost market growth during the forecast period
The Asia Pacific region is expected to play a significant role in boosting the market growth of probiotics in the animal feed industry during the forecast period. Asia Pacific has a rapidly growing livestock industry driven by population growth, urbanization, and increasing demand for animal protein products. Countries like China, India, and Southeast Asian nations have witnessed a substantial increase in meat consumption. As a result, there is a growing need for improved animal nutrition and health management, which fuels the demand for probiotics in animal feed.
The key players in this include ADM (US), Chr. Hansen Holding A/S (Denmark), Evonik Industries AG (Germany), Land O’Lakes Inc. (US), DSM (US), and Novozymes (Denmark). The study includes an in-depth competitive analysis of these key players in the probiotics in animal feed market with their company profiles, recent developments, and key market strategies.






